
You have brought your product or service to market and are generating revenue. You’re on your way to your dream career. However, there may still be bumps in the road that prevent you from collecting your receivables. For example, a customer’s NSF check. Not familiar with? Let’s consider the NSF check definition.
NSF stands for “not sufficient funds.” An NSF check is one that the issuing company’s bank refuses to accept because there aren’t enough funds in the account or the account has been closed.
For more information, keep reading.
Table of Contents
What Is An NSF Check?
The state of a checking account is indicated by an NSF (non-sufficient funds) check. A payee presents a check to the bank in this situation. The bank, however, does not accept that check. The reason for not doing so is simple, as the name implies.
Payment cannot be made because there are not enough funds in the payee’s account. As a result, the bank refuses to pay the payee at that particular time.
The payer’s bad intent is not implied by an NSF check. The payer typically provides the check, even though they may be aware that they don’t have enough money. An NSF check, though, can also happen for other reasons.
Among these, a timing difference is one of the most frequent causes. The issue and the check presentation differ in this way.
An NSF check might occasionally come with additional costs. The payer who hands the check into the bank is responsible for this fee. A fee for that fee might also be owed by the account holder.
In some circumstances, even if the account is insufficiently funded, the bank may still honor the check. Nevertheless, it overdraws the customer’s account by that sum.
In general, an NSF check refers to a check that is presented to the bank but is dishonored. It happens when a payer’s account is insufficiently funded to handle the payment.
In addition, the payer and payee may be charged fees for the NSF check. Checks can become NSF for a variety of reasons. But it’s important to know how to handle them in accounting.
Example
Summertime yard work for Tom is performed by Bill, a landscaper. Tom gives Bill a $100 check at the end of the month. Only $50 is available in Tom’s account, which is the only issue. To determine whether the check will clear when Bill goes to deposit it in his account, his bank may not always check Tom’s account balance. While also sending Tom’s bank the voided check, Bill’s bank credits his account with $100.
The tricky part comes at this point. When Tom’s bank receives the check, they determine that there isn’t enough money in the account and inform Bill’s bank that they won’t be transferring the money. A $100 debit is now made from Bill’s account by his bank, along with an NFS notification.
While Tom’s bank charges him $30 for having an overdraft account, they don’t like the fact that he wrote an NFS check. Tom is responsible for writing Bill a legitimate check and depositing an additional $50 along with the $30 overdraft fee into his checking account.
Terms Similar To NSF Check
An NSF check is also referred to as a bad check, bounced check, or dishonored check.
NSF Check Fees
A processing fee may be assessed by the bank to the entity attempting to cash an NSF check. An NSF check will undoubtedly result in a fee being assessed by the issuing entity’s bank. Another possibility is that the bank of the organization issuing the check will accept it and then charge the check issuer an overdraft fee. The entity cashing the check in the latter scenario won’t be assessed a processing fee by its bank because the funds have already cleared. See more about What Is A Returned Check Fee?
What Should An Owner Of An NSF Check Do?
A letter containing the check number, amount, and date along with all the information regarding the NSF check may be sent to the customer by the bank. As soon as the client receives a letter, they must send you a copy of it along with a letter outlining the issue.
In the event that you accept an NSF check, you might do the following:
Contact the customer – Receiving an NSF check can be easily resolved with clear communication. Your customer might occasionally unintentionally send an NSF check. By bringing up the matter with your customer, you give them the chance to pay you in full and keep your business relationship intact. You can also talk about any returned-check fees you paid and whether you anticipate getting reimbursed.
Write a demand letter – By sending a certified letter of demand, you can persuade a client to pay up before taking more drastic and costly measures. The formal letter might ask for the reimbursement of the check amount and any bank fees you were charged, as well as the specifics of the check and the reasons why it was returned. Set a firm payment due date with the customer. Make sure they understand that you’ll file a small claims court lawsuit against them if you don’t receive payment by the due date.
Hire a collection agency – You might want to hire a collection agency if your business frequently encounters NSF checks from the same clients. For a portion of the money your customer pays, these organizations assist businesses in collecting the money they are owed. Because the agency’s cut may be less than the cost of going to court, this method is useful for collecting small sums.
Take legal action – If your claim does not go over your state’s small claims threshold and the client refuses to pay, you may file a lawsuit. Since attorneys cannot represent you in small claims court, be sure to gather all pertinent documents, such as bank statements and receipts.
A company can take one of two legal actions against a client who attempts to pay with an NSF check. The state is aware that a NSF check can result in both civil and criminal consequences.
In most cases, the civil penalty, which is less severe, will establish the overall sum that the customer must pay your company in the event that they write a bad check. Since the customer is expected to pay any bank or court fees your company had to incur, the amount is almost always higher than the amount on the check. Additionally, a client may be held responsible for any additional losses your company may incur as a result of the NSF check.
The client may be arrested if charged with a crime. Because the checks were written with the intention of not honoring payment, a pattern of writing bounced checks may be regarded as fraudulent activity. However, because the issuers will pay as soon as they are made aware of their mistake, the majority of NSF checks are not criminally prosecuted.
Be diligent and professional in tracking down your payment. Sometimes all it takes to get paid is a phone call to a client or bank. Following several tries, you might need to look for outside assistance from collection agencies or a lawyer.
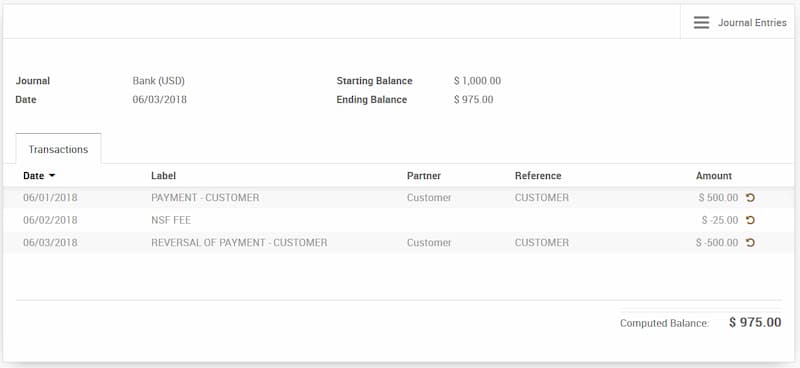
The Accounting Treatment Of An NSF Check
An NSF check is handled simply in accounting. Understanding how businesses record customer checks received is crucial, though.
Normally, once a business receives a check from a customer, it must record it in the accounting records. The prudence concept in accounting is supported by this treatment. Immediately after receiving a check from a customer, businesses account for it.
Companies are required to deduct the amount of checks they receive from their account receivable balance. Processing the check is not required, though.
Instead, businesses might deliver that check to the bank years later. Companies must record checks received for accounting purposes as soon as they are received. Companies are not required to receive the funds to their accounts in order to account for them.
Businesses will receive cash into their accounts after presenting the check to the bank. They might also be paid there in some circumstances. NSF checks, however, are an exception to the rule. The bank will refuse to pay the company in this situation.
It happens because the customer’s bank account is insufficiently funded to fulfill that request. Since businesses have already recorded that sum as a receipt from the customer, a problem has arisen.
Additionally, the bank might impose a fee for the presented check. That fee is due right away by the company. But because it has nothing to do with the business, the customer will be charged for that.
This sum is included in the check-nonpayment accounting. The amount due will eventually be paid to the business along with the bank charge. The customer is responsible for paying the NSF check fee as a result.
NSF checks are separately accounted for. When a check is received, it involves reversing the record of the first entry. It also affects two accounts. The first is the bank account where an organization has already noted a receipt.
The customer’s account is the other account, which the business reduced as a result of that receipt. Additionally, there is a fee paid to the bank in the form of an NSF fee.
Avoid An NSF Check
- Put a check handling policy in place and educate your employees on preventative check acceptance procedures, such as verifying customer identities and avoiding post-dated checks. Teach new employees to check that checks are filled out accurately and completely before completing a transaction.
- Ask your bank to notify you the first time a check bounces. Before informing you that there are insufficient funds in your checking account, banks can attempt to process a check twice. Saving time and letting your customer know more quickly will both be possible if you are aware of an NSF check the first time it fails to clear.
- Subscribe to a check authorization agency. These services enable you to scan checks at the point of sale to determine whether a customer has recently had bounced checks. You have the option to reject the sale if the customer has recently attempted to pay with NSF checks.
The End
When a bank check is rejected because there aren’t enough funds in the account, it’s known as an NSF check. Timing differences are just one of the causes that it could happen for. However, businesses are required to enter this sum as a reversal of the check receipt entry. They will also need to take into account any fees the bank assessed for the NSF check.
Many thanks for reading.


![Best Banks In California Top 11 Picks [2022]](https://www.findmybank.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Best-Banks-In-California-Top-11-Picks-2022.jpg)